
Local Anesthetics
Introduction
Local anesthetics are used to block nerve conduction, preventing pain sensation. They are used for minor procedures.
Local anesthetics can be used in place of general anesthetic to reduce nausea and vomiting, decrease cardiovascular risk, encourage earlier hospital discharge.
Indications
Local anesthetics are used for minor procedures, such as wound exploration and cleaning, suturing, fracture reduction, and excisions.
They can also be used intraoperatively to reduce pain during recovery.
Anesthetics with epinephrine are very useful for reducing bleeding at the site of injection via vasoconstriction. This can be especially helpful when attempting to visualize the field of view. Epinephrine also keeps the anesthetic local, allowing greater doses to be given by reducing the risk of systemic adverse events.
Clinical Usage and Tips
tip to remember amides from esters
amides: generic drug names have two I's
ester: generic drug has only one I
amide
- lidocaine (4-6 hours)
- bupivicaine (10-12 hours); slower onset
ester
- procaine
- cocaine
One can also give lidocaine and bupivicaine mix to provide rapid onset and longer duration.
Lidocaine can be quite painful subcutaneously; bicarbonate can be given at a 1:10 ratio. Slower injection can also help with pressure
Subcutaneous Injections
© 2006-2007 PocketSnips, Northern Ontario School of Medicine. (www.pocketsnips.org)
Video: Injection of Local Anesthetic. Used with permission.
The video is not a substitute for medical advice." |
Regional Blocks
Digital blocks
SIMPLE - single injection median palmar lidocaine with epinephrine.
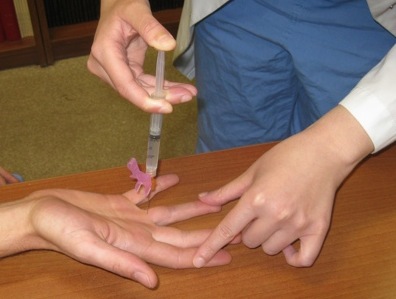
SIMPLE digital block, injected into proximal crease just above bone
- inject into the prximal crease of the palmar surface of the finger.
- Will cover entire volar finger and the dorsal side up to the PIP joint.
- better as there is only one injection
Dorsal block
- place your finger under theirs
- inject once you can see or feel tenting on their palmar side
Metacarpal block
- does the ray
- good for boxer's fracture reduction
- ensure you are not too proximal
- inject dorsally straight down until you see/feel tenting
- aspirate slightly before injecting
Hematoma block
Used for fractures; inject directly into the fracture hematoma. Often used by emergency room physicians and orthopedics, often under conscious sedation.
Median nerve blocks
Anesthesia can do a brachial plexus block, under local anesthesia and with ultrasound guidance.
Contraindications
People can be allergic to esters, but not amides. People CAN be allergic to the preservative in amides.
Lidocaine can be given at 7 mg/kg with epinephrine, or 5 mg/kg without.
It can be given in 1% or 2% solutions.
Local anaesthetics are lipid soluble and so can cross the BBB
As such, it is a good idea to keep local anaesthetics local!
Overdose and Adverse Events
Sigificant side effects can occur with lidocaine overdose, such as:
- peri-oral numbness (often first symptom)
- convulsions
- blurry vision
- allergic reaction
- metallic taste
Lidocaine overdose can be lethal following autonomic instability.
- tachycardia
- arrhythmias with lidocaine (even though that is what it is sometimes used for!)
There is no antidote for lidocaine, but there is for epinephrine.
Mechanism of Action
Esters are rapidly metabolized by blood esterases, so have a short half-life.
Amides are hydrolyzed in the liver, so longer/more varied half-life.
Additional Resources
Topic Development
created: DLP, Aug 09
authors: DLP, Aug 09
editors:
reviewers: